Threat Nix recently released a report called Threat report 2017 that covers and accesses the cyber attacks of 2017, to understand the situation of Nepal with respect to cybersecurity. Threat Nix is a group of security professionals who work to create cybersecurity solutions.
Why it matters:
The recent hacking techniques have become more sophisticated and Nepal has been a victim of a number of such attacks in 2017, among which only a few have become a matter of public knowledge. The report aims to increase awareness about the current state and vulnerability of cybersecurity of Nepal.
The Details:
According to the report, the major hacking incidents of Nepal in 2017 are as follows:
- On June 27, 2017, the official website of Department of Passport was reportedly hacked and defaced by a group of Turkish Hackers.
- On October 23, 2017, the SWIFT system of NIC Asia Bank was reportedly hacked by unidentified hackers. The hackers initiated a $4.4 million in fraudulent money transfers from its account to six different countries. The bank was successful in recovering $3.9 million after discovering suspicious transaction.
- On July 25, 2017, 58 government websites were reportedly hacked by a group called ‘Paradox Cyber Ghost’. Although the hackers group claimed it to be just a test, this was one of the biggest breaches of all times in Nepal.
- On November 28, 2017, OnlineKhabar was found to be using JavaScript mining application which uses the computer of anybody accessing the website to mine cryptocurrency called Monero. Later the mining script was removed and OnlineKhabar issued a press release attributing the activity to third-party malicious attackers on November 29.
Aside from these incidents, the report contains an analysis of various banks and devices that might be susceptible to illegal hacking.
Also See: Nepal and Cyber Security: A Review
According to the survey report, out of 27 e-banking sites of A-grade banks and 4 Payment Service Providers, the following statistics were obtained:
- 13 of those applications were vulnerable to Clickjacking.
- 4 e-banking sites were vulnerable to POODLE vulnerability.
- 1 application has a major security flaw that allows an attacker to steal funds from any logged-in victim.
- 1 application was revealing “phpinfo” and other 1 application had CRLF injection vulnerability.
Defacing is a common form of hacking, where the content of the hacked websites is replaced by some arbitrary content as desired by the attacker.
According to the survey report, a total of 756 “.np” websites were defaced in 2017.
- Out of which, 332 were commercial websites (.com.np), 160 were government websites (.gov.np), 133 were websites of educational institution (.edu.np), 123 were organizational websites registered in Nepal (.org.np), 4 were network operator websites (.net.np) and remaining 4 were co-operative websites (.coop.np).
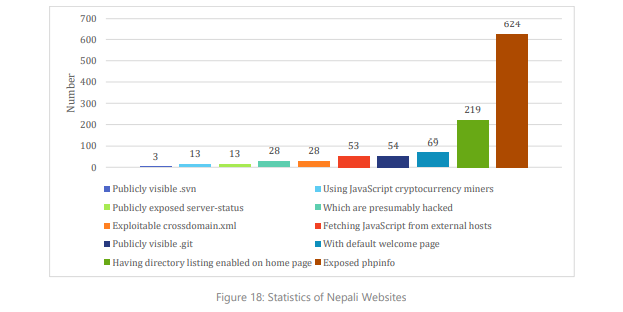
The report also contains the statistics of Nepali websites with respect to their susceptibility to being hacked.
Among the international threats, the report analyzes two major threats with respect to Nepal: WannaCry and HeartBleed.
- The report analyzed 82 devices in Nepal, among which 4 were found vulnerable, 54 were not vulnerable and 24 devices were throwing communication exception during the test.
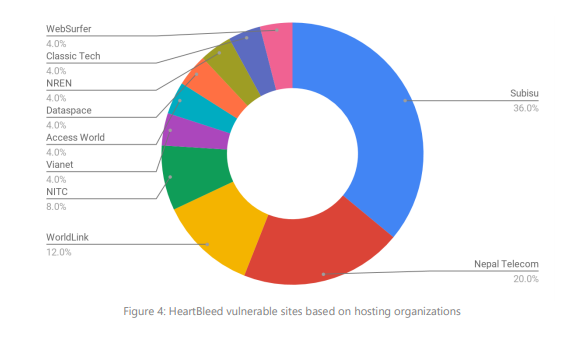
- The report found several instances of websites vulnerable to HeartBleed, belonging to different organizations and
their infrastructures, ranging from critical government infrastructures to ISPs’ websites.
The report categorized the vulnerable websites based on the organizations that host them.
Editors Recommendations
- Nepal Television Official Website Gets Hacked
- NIC Asia Bank Seeks Support From CIB to Hunt Down Hacker
- Nepal’s Official .np ccTLD Domain Registration Website Gets Hacked!
Read all the tech news of TechLekh. Stay updated!
-
New Bajaj Pulsar 150 Launched in Nepal with BS6 Engine and Single-Channel ABSHIGHLIGHTS Bajaj Pulsar 150 price in Nepal starts at Rs. 3.14 Lakhs and goes up…
-
MacBook Neo Coming to Nepal Soon: Apple Finally Makes an Affordable MacBookHIGHLIGHTS Apple MacBook Neo price in Nepal could start at Rs. 1,10,900 for the 8/256GB.…
-
Tecno Spark Go 3 Coming Soon in Nepal: FreeLink 2.0 is HereHIGHLIGHTS The Tecno Spark Go 3 price in Nepal could start at Rs. 16,999 (4/64GB).…